For the best skin care, it helps to understand what your skin is. As the largest organ of the body, the skin on the average adult contains:
- Weighs about six pounds
- 625 sweat glands
- 19 million cells
- On square inch of skin contains 94 oil glands
- 155 pressure receptors
- 19,000 sensory cells
- 1,250 pain receptors
- 60 hairs
- 19 feet of blood vessels
- 75 feet of nerves
- 12 heat receptors
Specialized cells and structures form a complex system of multiple layers of tissue. If any of the structures do not work properly, a rash or abnormal sensation may occur.
Don’t take skin for granted – as the primary interface between us and the environment. It is just as as the heart or brain. Skin can be permeated by many chemicals, which penetrating the skin may enter the bloodstream. Therefore, it is important to be careful to only use substances on your skin that will feed and nourish.

SKIN STRUCTURE
Three-different layers – epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis make up the structure skin
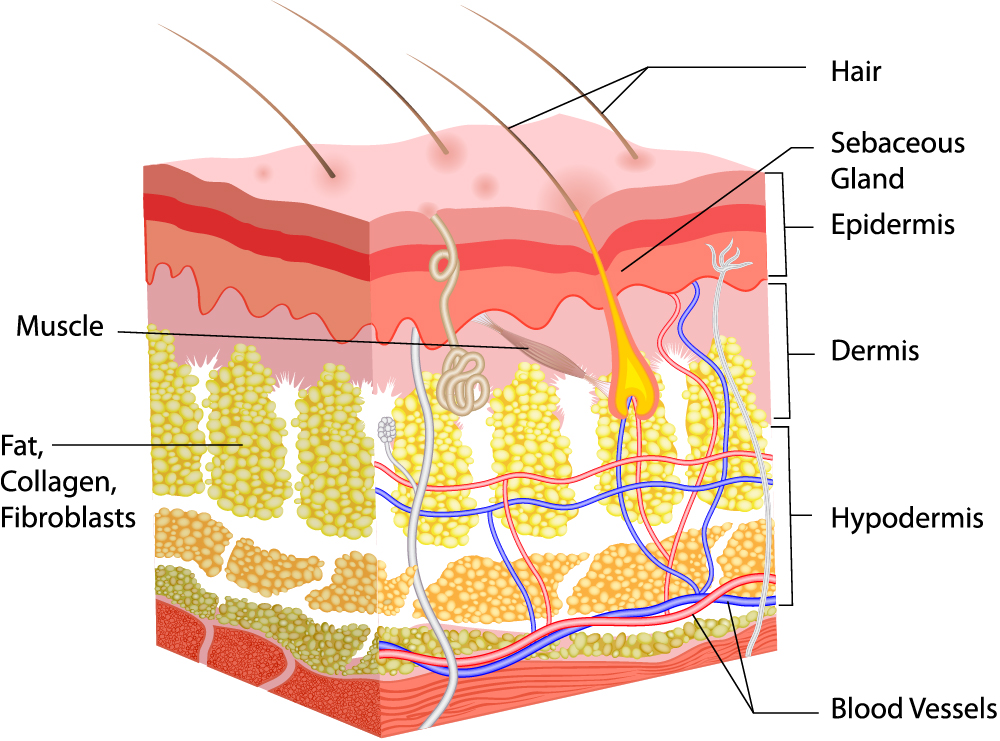
Epidermis
The outermost and first layer of protection of skin is the epidermis. The thickness of the epidermis varies on different types of skin. The eyelids are the thinnest layer at .05mm, while the layer on the palms and soles is 1.5 mm thick. This tough, relatively impermeable and self-replacing layer provides energy and insulation to the body.
Dermis
The dermis controls heat regulation, absorption and sensation as well as defensive reactions such as inflammation, and the healing process of growth and repair. The dermis also varies in thinkness depending on its location on the body. The dermis on the eyelids measures only about .3 mm thick, while the layer on the back is 3 times as thick as 3 mm. Tough collagen fibers and resilient elastic fibers provide mechanical strength. The dermis contains blood vessels that carry essential materials for growth, nourishment and repair to the skin, hair and nails.
Hypodermis
Made up of fat and connective tissue, the hypodermis supplies the skin with blood vessels and nerves. The hypdermis acts mainly as a cushion between the other layers of the skin and the underlying muscles, tissues, and bones.
Basket Cells
Surround the base of hair follicles and can senese pressure.
Hair Follicles
Nourish the hair
Hair Shafts
The part of the hair above the skin
Pacinian Corpuscles
Respond to pressure and vibration
Sebaceous Glands
Release a oily substance that coats and protects the hair shafts
Sensory Glands
Sense and transmit heat, pain, and other noxious sensations. When they are not functioning properly, one may feel sensations such as numbness, pain, tingling, or burning.
Sweat Glands (Sudoriferous Gland)
Produce moisture(sweat) secreted through ducts onto the surface of the skin. When sweat evaporates, skin temperature drops.









Skin ages in two different ways:
Intrinsic aging
Intrinsic aging is genetic (therefore impossible to delay or prevent)[1] and occurs over the entire body. The skin becomes thinner, drier, and slower to regenerate.
Photography
Photoaging occurs due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight. It is the main cause of cosmetic change to our skin as it ages. Photodamage results in a buildup of abnormal elastin which no longer has ‘springy’ properties and causes skin to sag and appear swallow, rough, and wrinkled.
A complex organ, skin plays an important role in our overall health, which is why it’s important to give your skin the best nourishment available. Your body (including your skin) regenerates. Given the right materials to work with it will heal itself and repair structures or cells that may not be working properly. MiraCell provides a line of products made from pure botanical extracts that helps your skin help itself – naturally. Whether or not you are afflicted with dry, rough, and scaly skin or not, MiraCell Skin Relief & support will give you the healthiest skin you’ve ever had



